Polio Outbreak in Malawi
This is the first case of wild poliovirus in Africa in more than five years. Malawi last reported a polio case in 1992. The country was declared polio free in 2005 —15 years before the African continent was declared the same.
Natural Disasters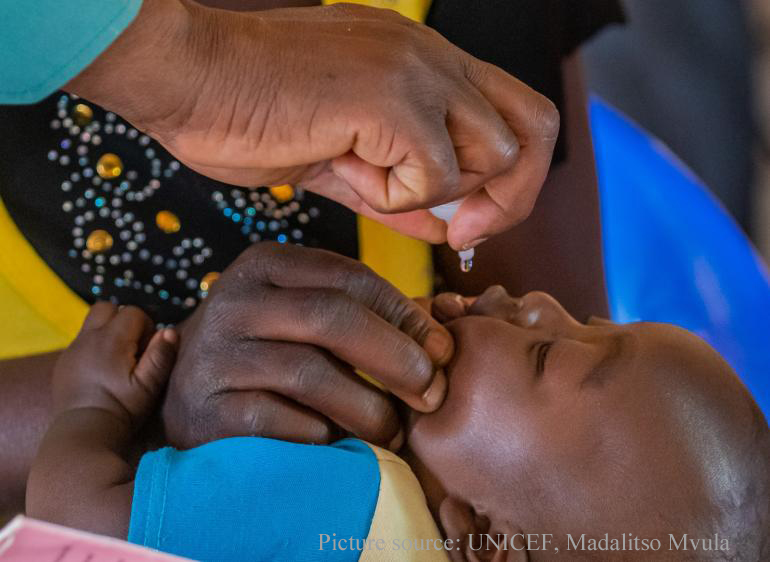
President of Malawi declared a National Public Health Emergency. Government has since launched a mass immunization campaign and vigilant surveillance.
The government of Malawi has currently launched an emergency response to the outbreak of polio. The plan includes mass immunization of children under five years of age and intensive surveillance to prevent the virus from spreading further.
This is happening after the President of Malawi declared a National Public Health Emergency on 17 February 2022, in response to the outbreak after a case was detected in the capital city, Lilongwe.
This is the first case of wild poliovirus in Africa in more than five years. Malawi last reported a polio case in 1992. The country was declared polio free in 2005 —15 years before the African continent was declared the same.
Deputy Minister of Health, Enoch Phale, said that despite the fact that the strain is imported, there is need for quick action against its spread.
He said: “We are doing whatever we can to ensure that we have broken the infectious circle. One of them is public awareness because its route of infection is two, water and food. And the disease is of global concern; it can affect everybody, including our neighbors.”
Polio is still endemic in three countries; Pakistan, Nigeria and Afghanistan and is eradicated from the rest of the world. Pakistan is considered as the exporter of Wild Polio Virus (WPV) with highest number of polio outbreaks among endemic countries.
Laboratory results link the strain in Malawi to the type in Sindh Province in Pakistan.
What is polio?
Polio is a highly transmissible virus most often spread via the stool of an infected person, usually through contaminated water or food. It can also be spread via oral or nasal secretions. The virus mainly affects children under five years of age.
There is no cure for the symptoms of polio. Most people infected with the virus have no symptoms at all, according to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). About one in four people will have mild symptoms that last two to five days, such as a sore throat, fever, fatigue, nausea, headache or stomach pain.
The virus usually stays in the gut, but when it spreads to other parts of the body it can cause more serious symptoms affecting the brain and spinal cord. These symptoms only occur in a small percentage of cases and can cause paralysis of some body parts, which can result in death if the breathing muscles become paralyzed, for example. This is known as paralytic polio.
